Fixed Ecological Sampling Station Surveys and Application of Ecologically Sensitive Information Maps
To support the Water Resources Agency (WRA) in implementing comprehensive improvement and adaptation plans for the 26 river basins under its jurisdiction, this project aims to build aquatic ecological intelligence maps, identify ecologically sensitive topics and species, and provide recommendations for ecological investigation needs based on the results. In addition to ensuring flood safety, the ecological information is used to mitigate potential ecological impacts caused by engineering activities—before, during, and after construction—so that flood safety and ecological conservation can coexist.
- Build Aquatic Ecological Intelligence Maps
- Develop ecological information maps for 26 river basins managed by WRA, as a baseline dataset to prevent or mitigate engineering impacts on habitats.
- Inventory and Integrated Analysis of Key Ecological Issues and Species
- Collect ecological data, evaluate critical habitats, and analyze sensitive ecological issues and species distributions.
- Assess and Recommend Ecological Survey Needs
- Based on analysis results, evaluate and propose necessary ecological surveys for each river basin.
- Conduct Targeted Investigations in Specific Basins
- Focus on Beigang River and Puzi River, reviewing existing species of concern and initiating targeted surveys.
- The purpose is to establish ecological baseline data, delineate ecologically sensitive zones, and support eco-checks during river management and engineering planning.
- Review and Refine Existing Ecological Survey Results
- Improve outcomes from both long-term ecological sampling stations and special survey projects.
- Establish and Analyze Aquatic Ecological Indices
- Propose a set of ecological indices suitable for evaluating aquatic ecosystem health within centrally managed basins.
- Promote Data Transparency and Application
- After compiling field investigation results, data validation forms are created and made publicly available.
- These ecological datasets serve as references for ecological reviews throughout the entire lifecycle of river engineering projects.
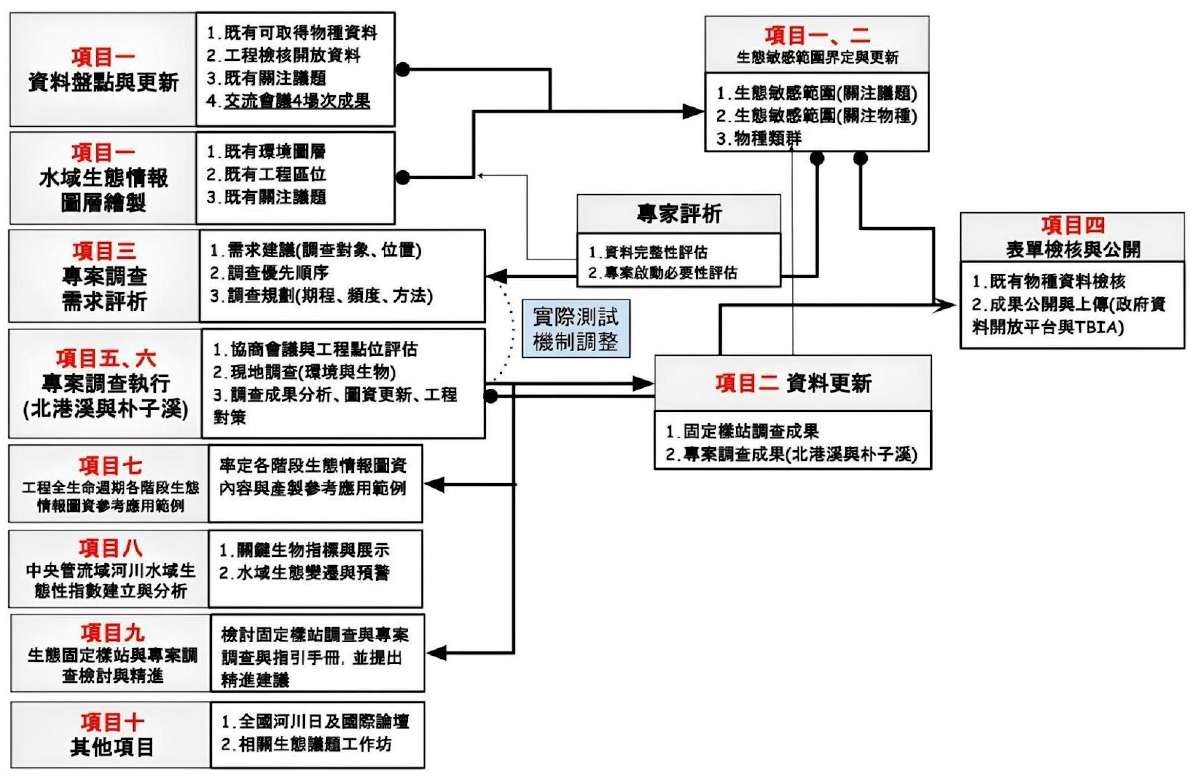
Figure 1 workflow and task structure.
Watershed Environmental Information Mapping & Application
In line with balancing flood control and environmental quality, the WRA has promoted the "Guidelines for the Production of Watershed Environmental Information Maps." These maps are fundamental for policy implementation, engineering planning, and local governance. The goal is to enhance map data quality and maximize application value.
- Improve Quality and Consistency of Mapping Data
- Review and correct submissions from regional river agencies.
- Integrate foundational GIS layers and improve verification workflows (including automated validation tools).
- Enhance Integration and Application Value
- Promote standardized and systematic approaches for map integration, data sharing, and cross-agency collaboration.
- Support national-level policy directions for Smart Water Management and Watershed Information Platform Integration.
- Align with National Policy Directions
- Extend previous achievements to support WRA's broader digital governance strategies.
- Promote Cross-Agency Data Sharing and Decision Support
- Strengthen cross-unit communication and planning efficiency using standardized, high-quality map data.
- Map packages and intelligence datasets provide a foundation for policy execution and resource allocation at central and local levels.
- Incorporate Public Participation and Local Insights
- Use tools like Google Maps and Google Earth during workshops and field visits to collect local feedback and improve map interactivity.
- Intelligence maps serve not only as data platforms but also as community engagement and issue reflection tools.
- Revise and Optimize Mapping Guidelines
- Based on actual verification, user feedback, and field experience, the guidelines are regularly revised.
- Revisions include:
- Simplifying map structure
- Reorganizing data categories
- Defining required vs. optional layers
- Streamlining content based on updated standards
- Public Education and Practical Promotion
- Outreach campaigns and educational materials enhance public awareness and participation in watershed and environmental governance.
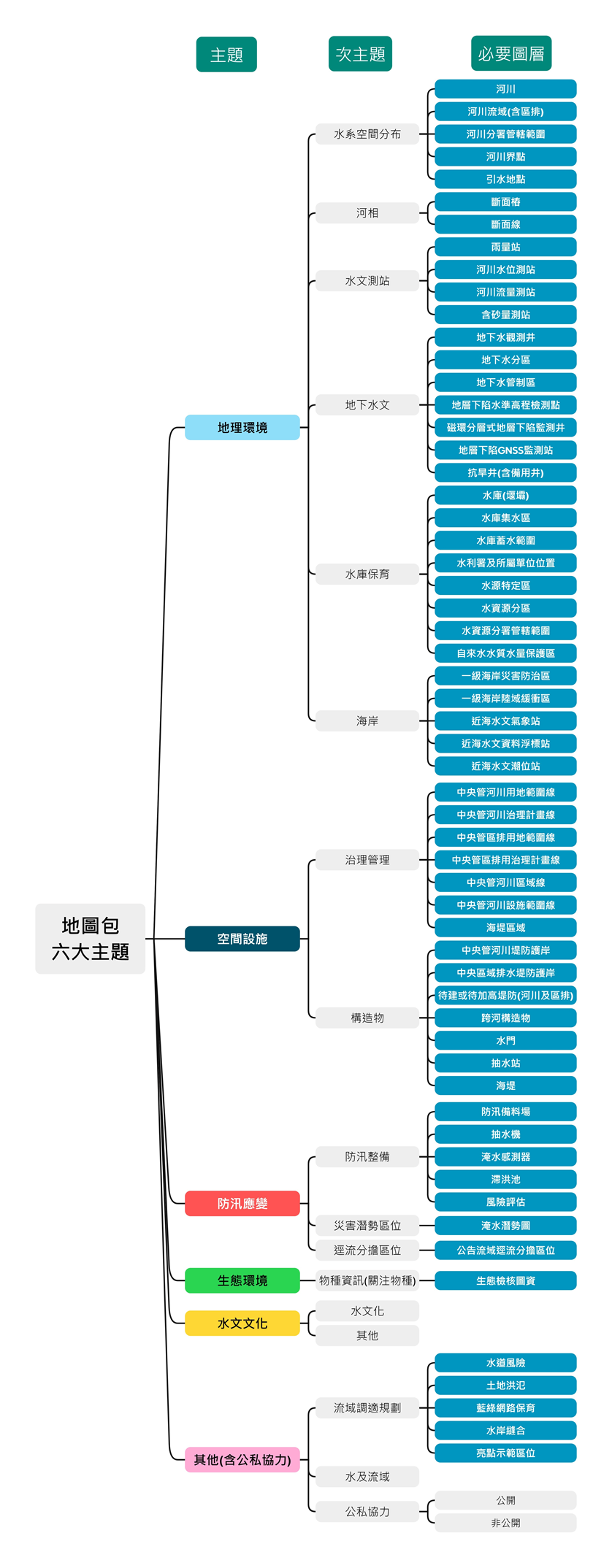
Figure 2 the map layer structure of watershed map packages.
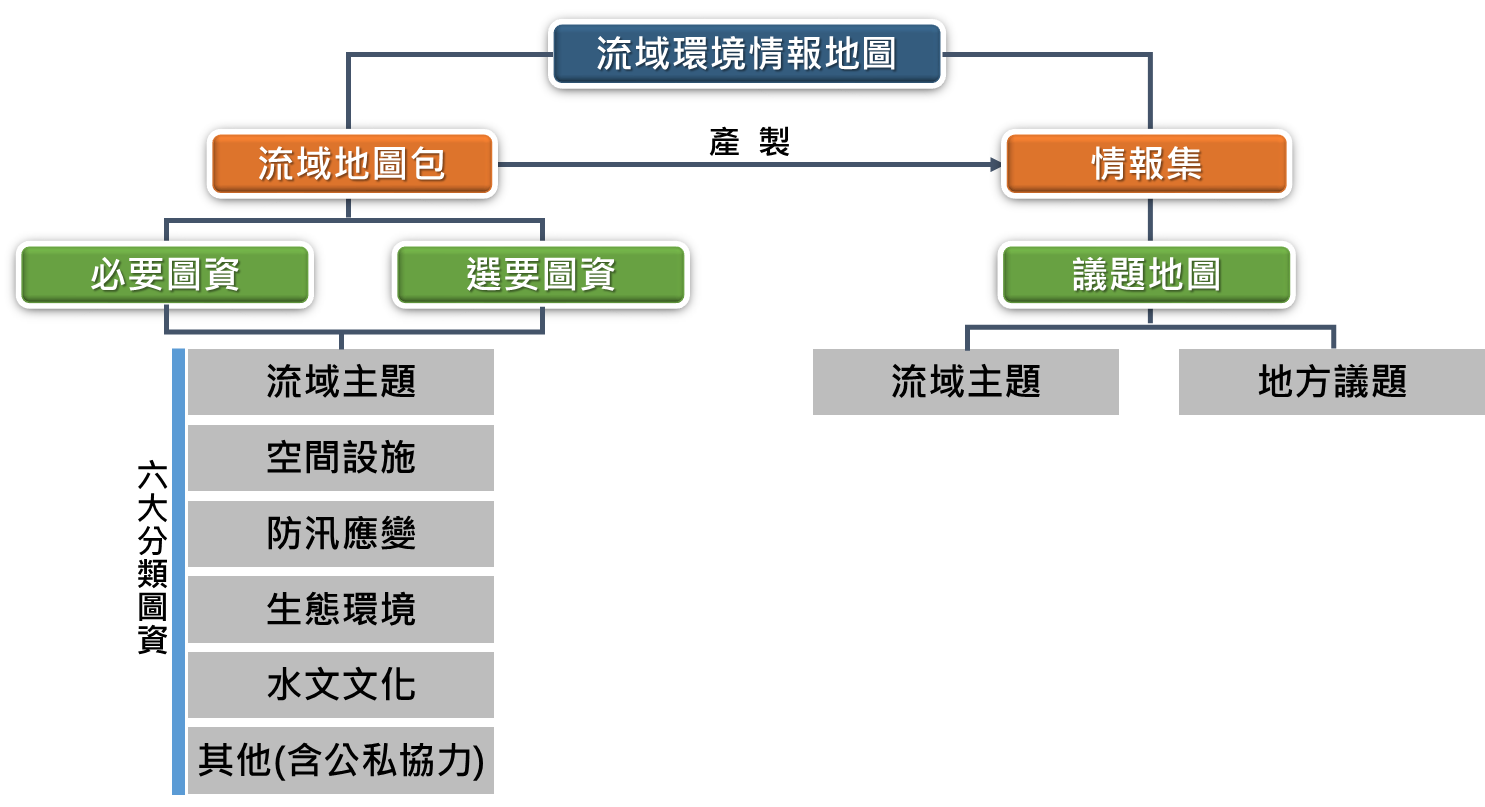
Figure 3 the thematic structure of the watershed environmental intelligence maps.