Climate Change – Flood Hydrology Scenarios and Application
To evaluate the impact of climate change on flood safety within central government-administered river basins, the Taiwan Climate Change Projection and Information Platform Project (TCCIP) downscaled rainfall data has been applied. This data serves as the foundation to establish a framework for climate change flood scenario analysis in Taiwan, providing essential reference for basin-wide adaptation planning and climate resilience strategies.
International Reference and Scenario Analysis
- Description of climate change scenarios and fixed-temperature pathways.
- Recommendations for the use and definition of Taiwan-specific hydrological climate scenarios.
- Impact evaluation of IPCC AR6-based climate and hydrological changes.
- Compilation and analysis of global and national-level impact assessment reports, including those from:
- The United States, European Environment Agency, Ministry for the Environment of New Zealand, Environment and Climate Change Canada, and the IPCC.
Rainfall Change Analysis for Central Government River Basins
- Analysis of rainfall change for 26 centrally managed rivers, considering:
- Mainstream length, watershed area, administrative districts.
- Presentation of results from:
- Dynamically downscaled rainfall impact analysis
- Statistically downscaled rainfall impact analysis
- Comparative study of different downscaling methods
- Characteristics of short-duration heavy rainfall events
- The appendix includes dynamic and statistical rainfall analyses for all 26 river basins.
Framework and Case Study of Downscaled Rainfall & Flow Analysis
Flood Hydrology Analysis Framework under Climate Change:
• The framework consists of two major parts:
- Rainstorm analysis
- Includes grid-mapping to control points, baseline and future frequency analysis, and scenario-based rainfall increment calculations.
- Use of statistical downscaling is recommended for better representation of climate uncertainties.
- Flood flow analysis
- Case studies are conducted to assess climate change impacts on design rainfall and flood discharges.
• Additionally, the analysis recommends integrating storm surge data from NCDR (with varying return periods) for riverine hydraulic modeling to assess climate-induced flood risks near river mouths.
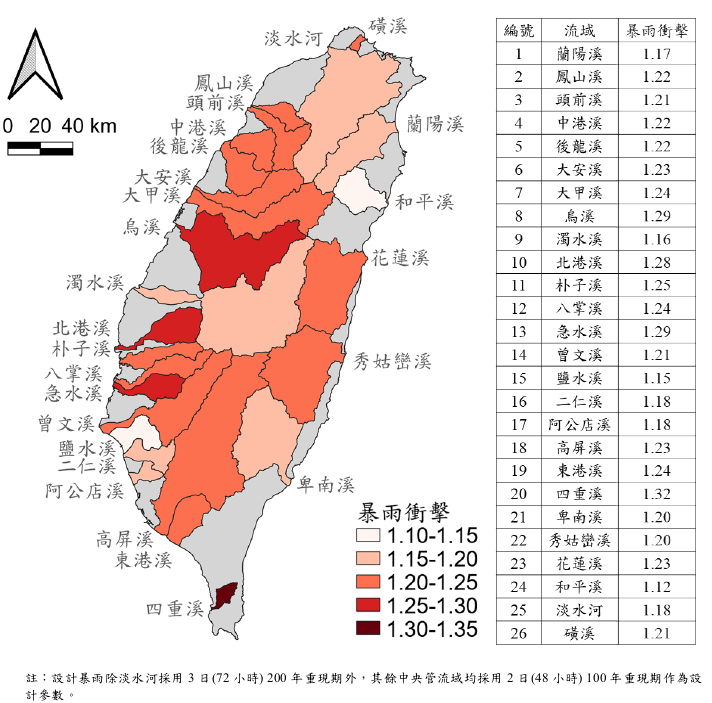
Figure 1: Impact analysis of statistically downscaled rainfall at river estuary
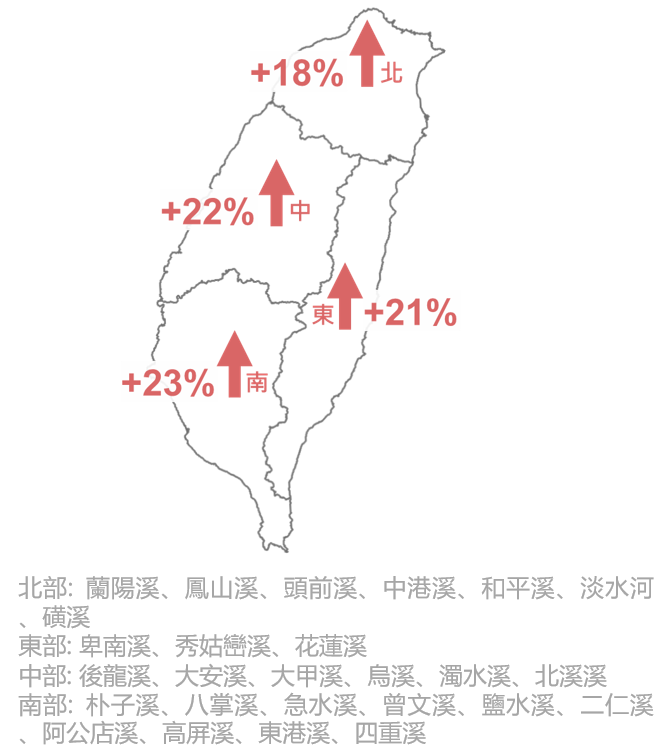
Figure 2: Two-day rainfall increase percentage for Taiwan’s four major regions
Development and Promotion of SRH-One 2D Hydrodynamic Model
Taiwan’s water environments are characterized by steep river gradients, rapid flows, and intense rainfall. These factors often lead to compound disasters such as flooding, landslides, and debris flows during typhoons or storm events.
As environmental and societal conditions continue to evolve, river management and water resource planning face increasing complexity. Therefore, numerical models are vital tools to support engineering analysis and decision-making.
To achieve the goal of comprehensive improvement and adaptation for centrally managed basins, including topics like channel realignment, floodplain management, green-blue network conservation, and waterfront integration, it is necessary to develop integrated watershed analysis models capable of both quantitative and qualitative assessment.
Model Development Goals
- Build localized watershed models suited to Taiwan's water environment
- Continue outcomes from Taiwan–US collaboration (Appendix VIII) to ensure effective technology transfer and application.
- Integrate multidimensional SRH modeling systems
- Combine SRH (Sedimentation and River Hydraulics) model series:
- SRH-1D, SRH-2D, SRH-3D, U2RANS, and in-development modules: SRH-W (watershed) and SRH-Coast (estuary).
- All models are adapted for Taiwan’s unique conditions (steep slopes, high flow velocity, extreme rainfall).
Enhancing River Management and Decision-Making
- Model-aided engineering analysis and decision support
- Numerical tools assist in quantifying the impacts of complex hazards and improving engineering strategy.
- Support integrated river basin improvement and adaptation planning
- Assist in quantitative/qualitative evaluations for policy and decision-making across various planning themes.
User-Friendly Interfaces and Documentation
- Development of SRH-One unified interface
- Simplifies SRH model operations and supports a variety of user experiences for engineers unfamiliar with multidimensional models.
- Localized user manuals and case studies
- Includes Chinese manuals and practical examples for SRH-1D, SRH-2D, and SRH-3D to enhance learning and application.
Promotion and Technical Support
- Expanding user base and model application
- Promote model usage among government agencies, consultants, researchers, and universities.
- Expand from SRH-2D to other modules (SRH-1D, SRH-3D, U2RANS).
- Professional training and technical consulting
- Conduct seed-user training, scenario-based model analysis, feedback integration, and application workshops.
- Provide ongoing technical advisory services.
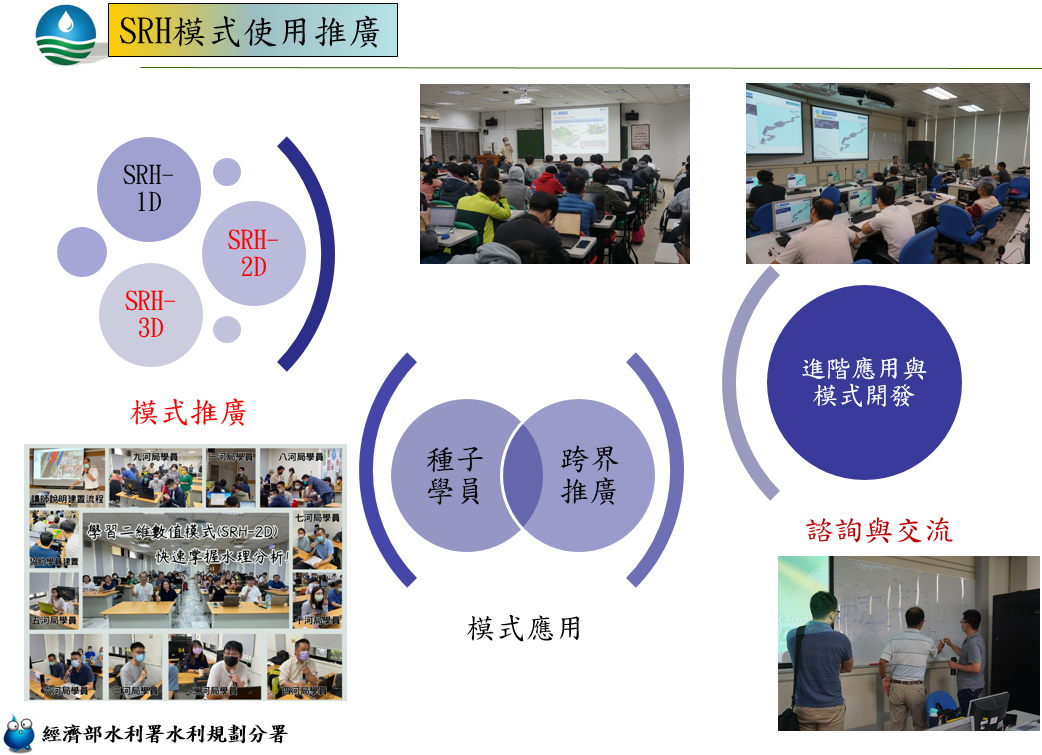
Figure 3: SRH model promotion and usage strategy
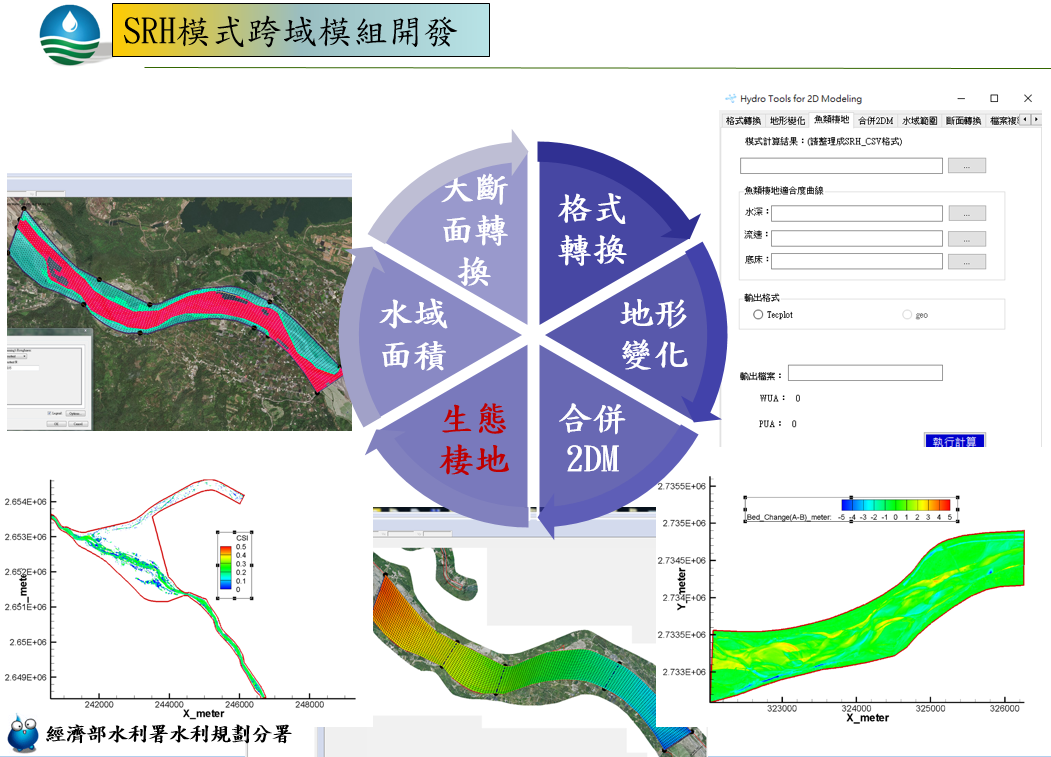
Figure 4: Cross-domain module development for SRH model system